
Decentralized identities in web3 have been a topic of discussion for quite some time now. In a decentralized system, the power to control data and identities is shifted from a central authority to the individuals themselves. Decentralized identities in web3 refer to a new way of managing identities online that puts users in control of their own data, instead of relying on third-party intermediaries.
In traditional web2, user identities are managed by companies such as Google and Facebook. These companies have the power to collect and use personal data for advertising purposes. In contrast, decentralized identities in web3 allow users to own and control their personal data, making it impossible for third parties to access or exploit it. This gives users more privacy, security and control over their online identities.
Working of Decentralized Identities(DiDs)

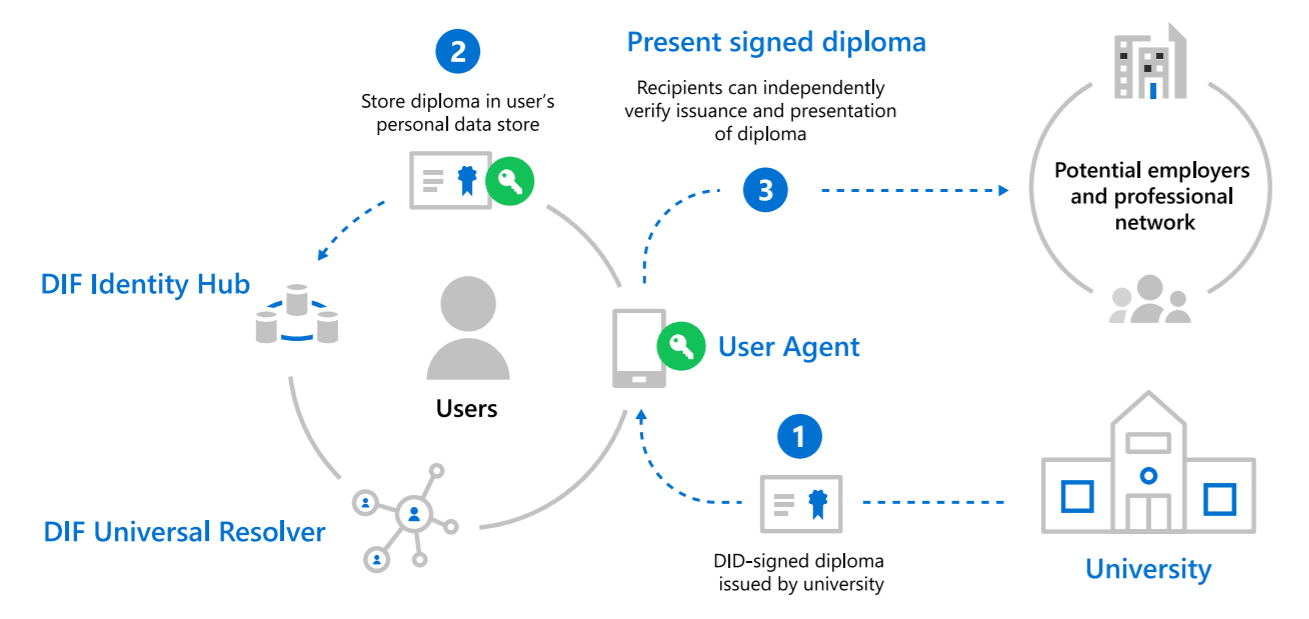
Decentralized identities in web3 work by using blockchain technology and self-sovereign identity (SSI) protocols. In this system, users create a digital identity for themselves, which is stored in a decentralized database. This database is maintained by a network of nodes, which are distributed across the internet. These nodes are responsible for ensuring that the data stored in the database is accurate and secure.
When a user wants to access a web3 application, they do so using their decentralized identity. This identity is verified by the network of nodes, which check that the user's data is accurate and that they are who they claim to be. The user's data is then encrypted and stored in the decentralized database, making it secure and tamper-proof.
One of the key benefits of decentralized identities in web3 is that they allow users to control their own data. In traditional web2, user data is often stored by third-party companies, who have the power to use it for their own purposes. In contrast, decentralized identities in web3 give users complete control over their data, allowing them to choose who they share it with and what it is used for.
Another important aspect of decentralized identities in web3 is that they provide more privacy for users. In a decentralized identity system, a user's data is encrypted and stored in a decentralized database. This means that only the user has the key to unlock their data, and it cannot be accessed by third-party companies or other entities. This enhances the privacy of users, as they can control who has access to their data and how it is used.
Future use case of DiDs


Financial Services
The future use cases of decentralized identities in web3 are diverse and far-reaching. One potential use case is in financial services, where decentralized identities can be used to secure and manage financial transactions. With decentralized identities, users can easily and securely manage their financial transactions, without having to rely on third-party intermediaries. This can lead to faster and more secure financial transactions, and it can also reduce the risk of fraud and other security issues.
Online Voting
Another potential use case for decentralized identities is in online voting. Decentralized identities can be used to ensure that only eligible voters are able to participate in an election, and to secure the results of an election. This can lead to more secure and transparent voting processes, and it can also help to reduce the risk of fraud and other security issues.
Healthcare Industry
Decentralized identities can also be used in the healthcare industry, where they can be used to secure and manage sensitive patient data. With decentralized identities, patients can control their own medical data, and they can choose who has access to it and how it is used. This can lead to more secure and private healthcare services, and it can also help to reduce the risk of medical fraud and other security issues.
Entertainment Industry
Finally, decentralized identities can be used in the entertainment industry, where they can be used to secure and manage the distribution of content. With decentralized identities, content creators can control the distribution of their content, and they can choose who has access to it and how it is used. This can lead to more secure and transparent content distribution, and it can also help to reduce the risk of piracy and other security issues.
In conclusion, the future use cases for decentralized identities in web3 are diverse and far-reaching. From financial services to healthcare and beyond, decentralized identities have the potential to revolutionize the way that data is managed and secured online. By giving users more control over their data and enhancing their privacy, decentralized identities in web3 offer a more secure and private way of managing data online.
Examples of DiDs
uPort
There are many examples of decentralized identities in web3, each offering its own unique set of features and benefits. One well-known example is uPort, which is an Ethereum-based decentralized identity platform. uPort allows users to create a self-sovereign identity that they can use to access a wide range of web3 applications. With uPort, users have complete control over their data, and they can easily share it with others when needed.
Civic
Another example of a decentralized identity platform is Civic, which uses blockchain technology to secure and manage user identities. Civic provides a secure and transparent way for users to manage their personal information, and it also offers advanced security features to protect users from fraud and other security threats. Civic is well-suited for use in industries like healthcare, where security and privacy are of utmost importance.
Polygon ID
Polygon ID is a decentralized identity platform built on the Polygon network. It allows users to create a digital identity that is secure, transparent, and tamper-proof. With Polygon ID, users can control their own data, and they can choose who has access to it and how it is used. Additionally, Polygon ID is designed to be highly scalable, making it well-suited for use in large-scale applications.
Evernym
Finally, another example of a decentralized identity platform is Evernym, which is built on the Sovrin network. Evernym allows users to create a secure and private digital identity that they can use to access a wide range of web3 applications. With Evernym, users have complete control over their data, and they can easily share it with others when needed. Additionally, Evernym is designed to be highly secure, making it well-suited for use in sensitive applications like healthcare and financial services.
Implementation of Decentralized Identity
Implementation of uPort
// Import the uPort library
const uPort = require('uport-js');
// Create a new uPort identity
const uportId = new uPort();
// Request information about the identity
uportId.requestCredentials({
requested: ['name', 'email', 'phone'],
notifications: true
})
.then((credentials) => {
// Store the information about the identity
console.log('Credentials:', credentials);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error('Error:', error);
});-
In this example, we start by importing the uPort library. Then, we create a new uPort identity using the
uPortconstructor. Next, we use therequestCredentialsmethod to request information about the identity. This information may include the user's name, email address, and phone number, and it is requested with therequestedoption. -
Finally, we use the
thenmethod to store the information about the identity, and thecatchmethod to handle any errors that may occur.
Implementation of Polygon ID
// Import the Polygon ID library
const PolygonID = require('polygon-id');
// Create a new Polygon ID client
const polygonID = new PolygonID();
// Create a new identity
polygonID.createIdentity().then((identity) => {
// Store the identity
console.log('Identity:', identity);
});
// Request information about the identity
polygonID.getIdentityInfo(identity.address).then((info) => {
// Store the information about the identity
console.log('Identity Info:', info);
});-
In this example, we start by importing the Polygon ID library. Then, we create a new Polygon ID client using the
PolygonIDconstructor. Next, we use thecreateIdentitymethod to create a new identity. -
Once the identity is created, we use the
getIdentityInfomethod to request information about the identity. This information may include the user's name, email address, and phone number, among other things. -
Finally, we use the
thenmethod to store the information about the identity and the identity itself, and thecatchmethod to handle any errors that may occur.
This is a simple example of how to implement a decentralized identity in a practical form, but it can be expanded and adapted to meet the specific needs of your application. With decentralized identities, you can easily manage and secure your user data, and you can also enhance the privacy and security of your users.
Conclusion

In conclusion, decentralized identities are a key component of the emerging web3 ecosystem, providing users with more control over their personal information and enabling more secure and private online experiences. Decentralized identities work by leveraging blockchain technology to store and manage user data, ensuring that this information is tamper-resistant and always under the user's control. The future use cases for decentralized identities are virtually limitless, ranging from secure access to online services and financial transactions, to seamless data sharing and collaboration in decentralized networks.
Examples of decentralized identities include the uPort platform and the Polygon ID solution, both of which offer powerful tools and resources for developers looking to implement decentralized identities in their applications. With code examples available, it has become easier than ever to implement decentralized identities, providing users with more control over their data and enabling a more secure and private online experience. As decentralized identities continue to gain traction and evolve, they will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of the web and the internet as a whole.